Strategy – that’s a very complex thing, isn’t it? Let’s not worry about what’s going to be a corporate strategy or war strategy or anything. Given that we are software engineers, let’s focus on “Strategy” design pattern and it’s advantages.
Sidecar
Sidecar is a design pattern that allows deploying a supplementary service alongside the main application on the same host. It is a very popular pattern in microservices architecture and provides isolation to the main service from failures in supplementary services if any.
Circuit Breaker Pattern
As the name suggests, the “circuit breaker” is a design pattern in software architecture, which has gain prominence in the distributed environment.

Circuit Breaker Pattern in detail
Almost each one of us knows about the MCB – miniature circuit breaker that is used in our homes. Its function is to break the electric supply of a particular circuit – either of a room or of an entire house – if it detects some anomaly in the electric supply or usage. Once the anomaly is removed, we can restore earlier state and the electricity resumes.
In this design pattern, there’s a component named “Circuit Breaker” which does exactly same. It acts as a proxy for certain function/API calls. If the call fails beyond a certain threshold, this component starts returning an error to the caller, even without checking if the proxied function/API is working.
Unlike MCB, this being a software component, it can be made more intelligent. This Circuit Breaker component can have a threshold and timeout defined. Once the error rate crosses the threshold, the component starts returning an error to the caller for a timeout period. After that, it tries to call the proxied function/API few times. If successful, it can slowly resume the service over a period of time.
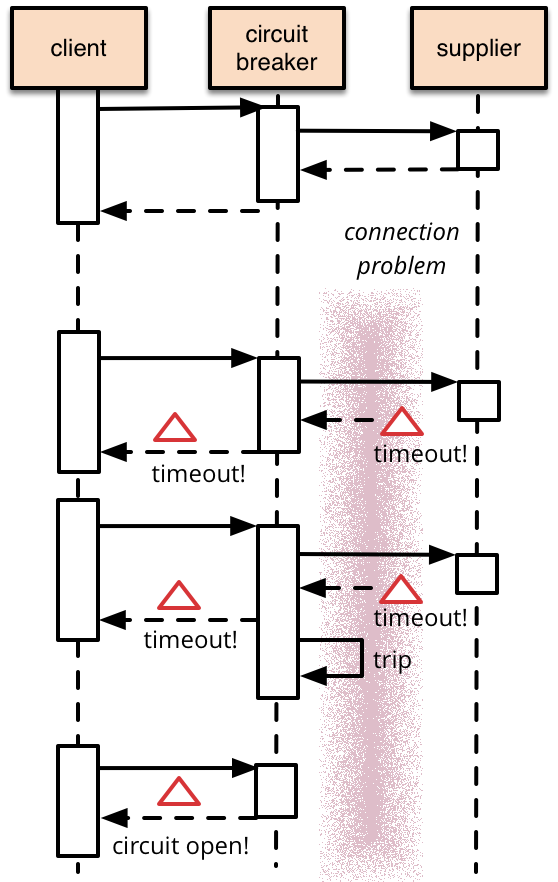
But, wait, wouldn’t it cause a problem for the users?
It could. However, in the distributed architecture, failure is always a possibility. This design pattern teaches to embrace failure rather than denying the possibility of failure. The overall architecture can handle such failures gracefully. e.g. if a service providing recommendations for titles of movies or books, you could easily show something else or not show anything at all. That would still allow your users to use the overall application – albeit w/o some functionality. This would anyway be better than failing entire application.
Also, the component can include the monitoring feature as well. This can push data about the failure rate to a central dashboard, which will allow administrators to check the failed components and take corrective measures.
Example of Circuit Breaker Pattern
Netflix has implemented this pattern very effectively and has also released the library which provides various functionalities they are using internally – Hystrix. There are some very good articles available which are mentioned in the links below.
Related Links
- Circuit Breaker Design Pattern
- Martin Fowler Article
- Hystrix – Netflix Tech Blog
- Hystrix – Github
- Implementing Circuit Breaker Pattern with Nginx Plus
Related Keywords
Microservices Architecture, Hystrix, API Gateway
Material Design
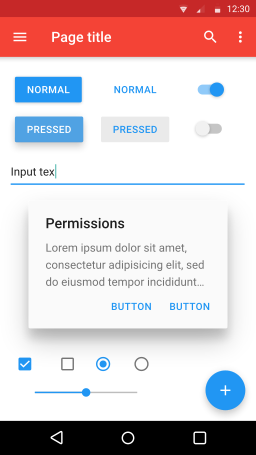
Don’t get worried by reading the subject. This is not about any civil topic or interior design work. Material Design is a design concept introduced by Google which is prompting designers to rethink the web and mobile app UI. Here material is a metaphor. It is used to help you visualize web or mobile app as a physical object which has it’s own properties and responds to touch, zoom, pinch etc. Applications following material design present uniform behavior across various applications as well as various sizes of devices, thus giving uniform experience to the user.
Where can I see Material Design in action?
If you are on the android phone, it is everywhere in native apps (Android 5 onwards). When you use Chrome browser, check out settings and you will see it there. If you click on a text field, the placeholder quickly moves to top left. If you click on a tab, the bottom border of the tab is highlighted. The buttons have a shadow effect giving a feeling of depth. All such things are based on Material Design principles.
So what are the principles, this is based upon?
- Each component occupies its own layer as if two physical objects are kept one on top of the other. They will not merge with each other, nor will the pass through each other. In simple terms – they appear as 3D objects.
- Visual effect on one component will not follow through on other objects.
- Some components would react to action (like touch, swipe, zoom etc) faster than others.
- Every user interaction with the screen gives instant feedback to the user in terms action happened.
- Components are aware of their surroundings. E.g. Upon touching a button, it pushes out certain components to make the place for the input field.

Similar to Bootstrap, there are several components pre-built and available for use to the developers. Refer to this article which has excellent comparison between Bootstrap and Material Design
In addition to Google’s own documentation, there are some very comprehensive articles about this design, check reference section below.
Related Links
Related Words
Bootstrap, Mobile App, Web App, Design, CSS