What is ejabberd?
Ejabberd is an open-source XMPP server/messaging platform written in the Erlang language. It is used to power real-time applications and also used to provide communication services such as instant messaging, group chat, presence, multi-user chat, and file transfer.
What are the typical use cases?
The most common use cases include:
- Instant Messaging Applications: Enabling users to communicate in real-time within corporate networks or between two or more remote systems.
- Presence Status Updates: Providing an interface for users to update their availability and see their contacts’ status.
- Group Chat: Allowing users to participate in group conversations with multiple-user chatrooms.
- File Transfer: Allowing users to send and receive securely
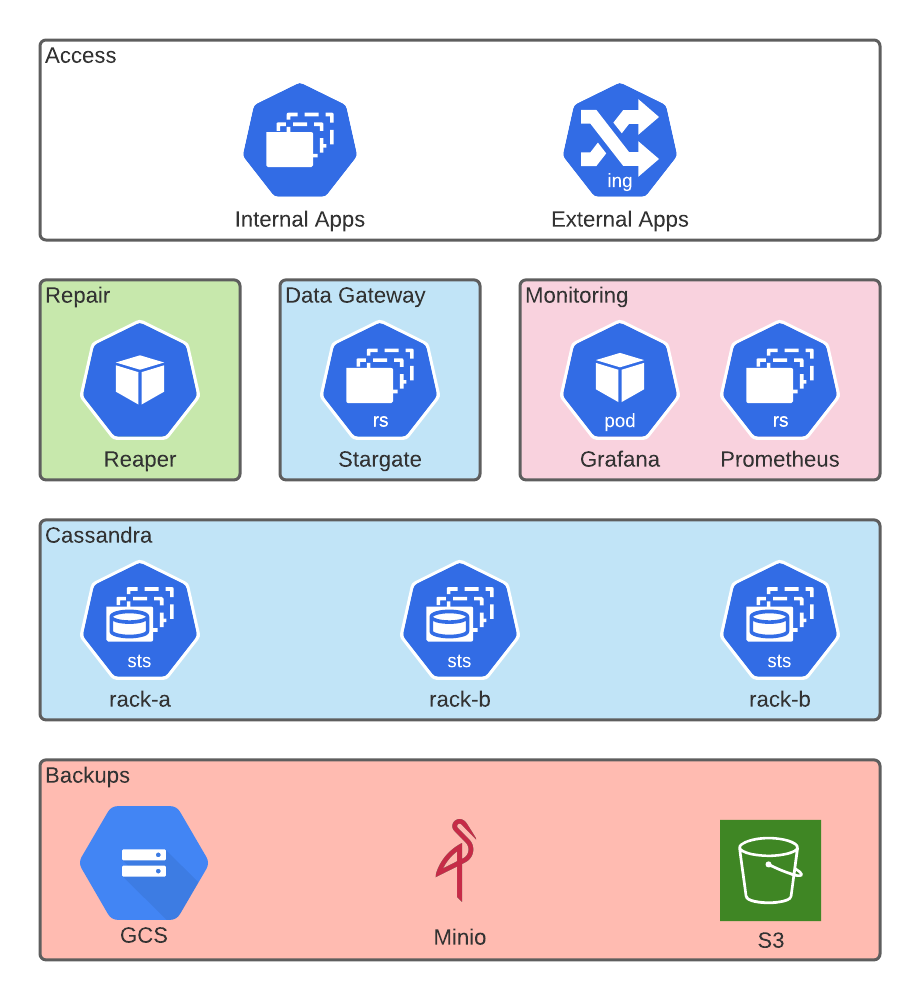
Architecture

Alternatives:
Alternatives include Openfire, Prosody, Tigase, and Matrix.
History of ejabberd
Alexis Moura developed it in 2002 and continued to lead the project until 2009 when ProcessOne took over. Since then, it has become one of the most popular and widely used messaging platforms in the world. It has been used in various projects, from small-scale private messaging applications to large-scale deployments with millions of users.
Usage of ejabberd:
Many leading organizations and companies, including Facebook, Microsoft, Google, WhatsApp, Apple, Amazon, and Twitter use ejabberd. Additionally, many open-source projects and products, such as Openfire, Prosody, Tigase, and Matrix, are built on top of this platform. The primary reasons for its usage are:
- Scalability: It allows for horizontal and vertical scalability and can support up to one million concurrent connections.
- Security: It includes a range of security measures to ensure data integrity and user privacy.
- Reliability: It is a robust and reliable platform that is resistant to excessive load and can remain operational 24
Related Links
- Home page
- Comparison between various XMPP tools
- How To Build One To One Chat App Using Ejabberd & Erlang From Scratch?